Russia's Economy Shrinks as Sanctions Bite
After the collapse of the Soviet Union, Russia has made a great development in their market-based economy. And they established their economy as a global economic power. The Russia-Ukraine conflict harms Russia’s image and economy.
Until 2020, Russia has the world’s sixth-largest economy. Russia’s current geopolitical and economic condition is the result of a lengthy and convoluted history. After the invasion of Ukraine Russia has been isolated from most of the international financial and commerce system.
Even though Russia's GDP grew by 3.5% annually during 21-2022, the nation is currently entering a period of recession.
Russian Economic Features
The natural resources contribute a huge part of the national economy. But natural resources are not just the only factor that motivates the country’s money and the people. Some other aspects are included in the Russian economy.
Many States participated in the development of the national economy and many government officers got benefits from this contribution and made a huge amount of money.
Russian currency is called the ‘Ruble’. The ruble price is significantly low in comparison with the USD($). One Russian ruble is equal to 0.016 dollars.
In 2021 Russia’s GDP was around 1.78 Trillion.

According to Google information 143.4 million people reside in Russia. A large number of this population are seeking employment. A huge amount of the residents who looking for employment. And it is about Seventy-one million and Eight hundred and Eighty-five thousand residing
After the invasion of Ukraine, the sanctions were implemented in 2022. Cars and automobiles, packaged medications, Chemicals, and broadcasting equipment are the top imports. Importing in Russia decreased to 23503 USD Million in October from 24725 USD Million in September of 2023.
What Does the Term "Sanction" Mean?
Sanction is established to maintain international stability. The term sanction is established as the alternative to armed intervention. It is the most common tactic used for the guilty state or organization. Economic, diplomatic, individual, military, or cultural restrictions are all included in the sanctions.
Trade barriers, asset freezes, and banking prohibitions are all examples of economic sanctions (Radcliffe, 2022). Sanctions against a person may include a ban on travel or a limitation on their ability to access their money or property. Sanctions on the armed forces may halt military training abroad and the sale of weapons.
Refusing to provide visas and other diplomatic benefits is a typical kind of diplomatic censure. Prohibiting persons from participating in international competitions or exhibitions is an example of a cultural sanction.
Sanctions are put in place with the hope that they would reduce the power of the government or political elite by cutting off their funding and other resources (Bossuyt, 2012). In principle, this will undermine the authoritarian system by reducing the group's ability to maintain control.
Who Implements Sanctions?
States and regional powers like the E.U. or the U.N. may apply sanctions. Article 41 of the UN Charter gives the Security Council and the E.U. the power to impose non-military sanctions (Pydiamah, n.d.).
Since 1966, the Security Council has utilized Article 41 30 times, sanctioning South Africa, Somalia, Al-Qaida, and the Taliban. E.U. sanctions number over 40. (The European Commission, 2022).
Russia Sanctions
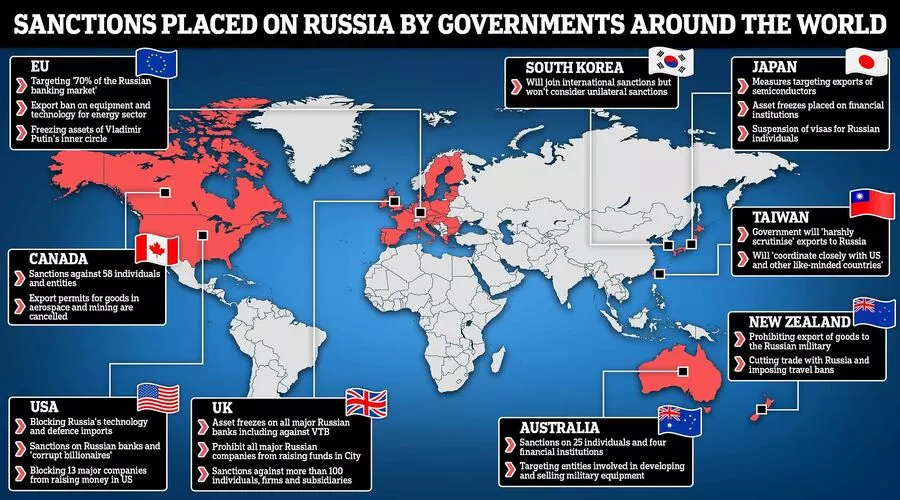
Recent E.U. sanctions on Russia and Belarus are in response to the Russian invasion of eastern Ukraine (The European Commission, 2022a). These restrictions restrict bank access, prohibit bank transactions, bar Belarus firms from E.U. trade markets, and limit Belarusan deposits in E.U. banks.
Russia also faces sanctions. Russia's marine, radio, and crypto-asset technology have been restricted. 862 Russian persons and 53 Russian businesses are subject to E.U. sanctions.
The U.S. has blocked Russian oil imports and sanctioned its central bank (Walsh, 2022). Individual enterprises have also reacted to Russia's incursion. Starbucks, Coca-Cola, McDonald's, Disney, IKEA, M&S, Bumble, and Warner Bros. have all gone out of business in Russia (Bokat-Lindell, 2022). Amazon does not accept new service sign-ups (Weise, 2022).
Economic, diplomatic, interpersonal, military, and cultural sanctions target Russia. Russian athletes are barred from competing in the Olympics and FIFA. The French economics minister called the fines "an economic and financial war" (Walsh, 2022).
How Have Sanctions Affected the Russian Economy?
Russian aggression on Ukraine in February 2022 was completely unprovoked and justified, but it has not stopped the Council from passing eight sanctions against Russia and Belarus. The sanctions are directed at Russia's political, military, and economic elites, who are responsible for the invasion and try to impair their capacity to fund the war.
Russian Society is not an intended target of the restrictions. So sectors like food, agriculture, healthcare, and pharmaceuticals are not included in the sanction. Restriction on Russia is affecting according to the estimations. And it was demonstrated in some of the analyses of a variety of sources.
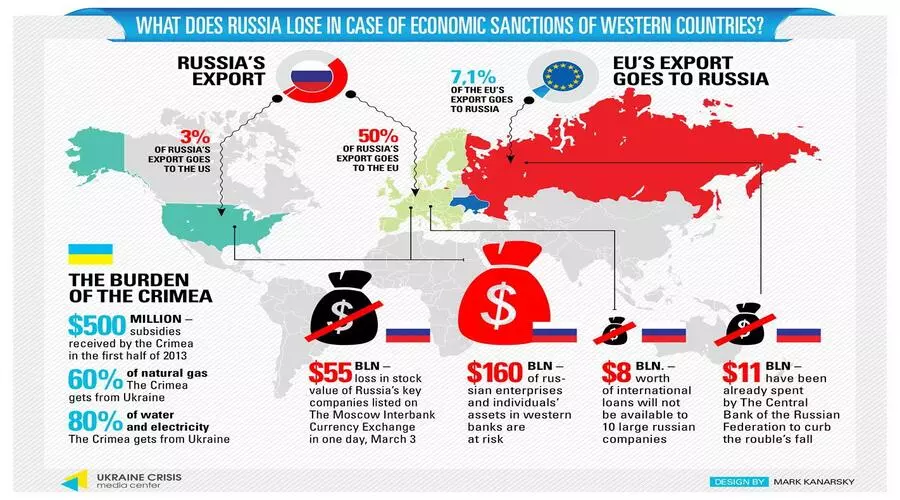
It is predicted that by the end of 2022 Russian GDP will fall by 3.4% to 4.5% at the very most. International organizations such as the IMF, World Bank, and OECD also agree that 2022 will be a poor year for the Russian economy. At the end of the year, the national GDP is Shrink 2.1%.
In 2023, Russia's economy will contract even more. Forecasts place the annual rate of reduction in its GDP at 2.3%, with a maximum of 5.6%. Certain items are the focus of the restrictions placed on the trade.
The purpose of the sanction is to gain the most effect on the Russian economy. And having the least negative impact on E.U. firms and individuals.
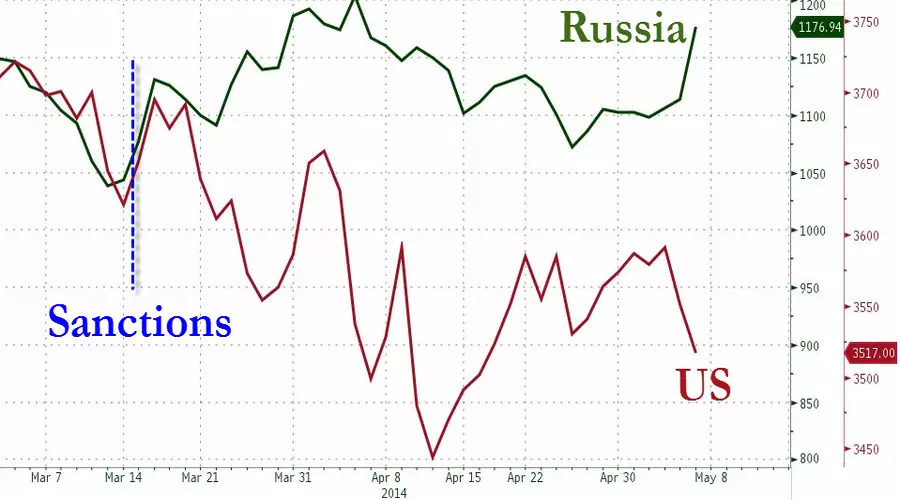
The effect of restrictions has been shown by numbers. Imports are estimated to increase from 2022 levels and the exports continue to fall and the Russian GDP’s gross domestic product.

Sanctions Affected the Russian Economy, Russia's Economy Shrinks
The World Bank and IMF both predict that Russian merchandise and services exports sharply decrease by 2022. Russian GDP decreased by 2.1% at the end of 2022.
It was predicted that the inflation rate would have skyrocketed by about 14% by the end of 2022. The average inflation rate in 2022 was 13.77 % compared to the previous years. Predictions for 2023 from 5% to 6.8%. The inflation rate in Russia was 5.28% in the year 2023. And it has increased in the year to 6.34%.
Russian businesses are also affected by the conflict and sanctions. Since February the Moscow Exchange’s main index has dropped by more than a third.
Is There Any Alternative to Sanction?
The Russian invasion of Ukraine has reached a tipping point, and it may amount to criminal acts (Khan, 2022). Therefore, recent occurrences question how Russian aggression can be deterred without harming Russian civilians. Sanctions may not be as effective as hoped, but they will hopefully prevent more harm to international stability.
Besides penalties, what non-interventionist options exist? Professor Mulder proposes a change in the conventional carrot-and-stick approach, basing his argument on the work of economist John Keynes. He thinks the international community should provide Ukraine with the "carrot" of economic aid instead of the "stick" of sanctions.
He elaborates, "All nations confront a mix of interrelated difficulties: supply chain problems, uneven income, vaccination distribution, and accelerating climate change." When faced with such a scenario, it is better to use the positive instrument of help than the destructive weapon of penalties (Mulder, 2022).
The international community's resolve to aid Ukraine has grown in tandem with Russia's aggressive behavior against the country. The United Nations Congress recently approved $13.6 billion in help (Edmondson, 2022), all 27 member states of the European Union have provided money (European Commission, 2022b), and the World Bank is negotiating a $3 billion aid package (BBC, 2022).
Final Thoughts
Because of the Russian invasion of Ukraine, their economy has suffered. and it makes the foresee of the collapse impossible.
International economic experts of the OECD predicted that Russian GDP will drop a 3%. And the GDP of Russia dropped by 2.5%.
However, the shrinkage of the Russian economy affects the other countries' economies as well. This will end soon, and the whole world, especially people from Third World countries, will get relief within the shortest time possible.
Our Latest Articles-
Global Impact of Russia-Ukraine War
FAQ
How does the Russian invasion impact the U.S. economy?
According to the Dallas Fed, the U.S. economy should be less impacted by the Russian invasion than other nations. The U.S. trades less with Russia and produces much energy domestically. Global cost increases will cause inflation and economic slowdowns here.
What are Russia's demographics and products?
Russia is the world's biggest country, with 17 million km2. Russia's oil, gas, and metals industries are robust, but its population is aging. The birth rate is 9.45 per 1,000 people, one of the lowest in the world. The median age is 40, which is younger than in Europe but older than in the U.S.













